New Joining and Additive Manufacturing Processes Allow Adhesive-Free Joining of Wood and Metal
The renewable raw material wood is climate-neutral and at the same time light and strong, making it fundamentally attractive for use in vehicle manufacturing. One challenge to date has been joining the wood and the other materials in the vehicle, such as metals and polymer composites, in a robust way. The research team led by Sergio Amancio from the Institute of Materials Science, Joining and Forming of Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) – Gean Marcatto, Awais Awan, Willian Carvalho and Stefan Herbst – has now successfully tested two techniques by which extremely strong joints can be achieved without using adhesives or screws. The application of the techniques to wood is patent pending and could be used in the aircraft, automotive and furniture industries.
Joining technology and additive manufacturing enable wood to replace less sustainable materials
The two novel manufacturing techniques are suitable for their own areas of application. Beech, oak, carbon fibre-reinforced polyamide and polyphenylene sulphide, stainless steel 316L, and Ti-64 alloys, were used as test materials. “Our motivation is clearly environmental protection,” says Sergio Amancio. With new manufacturing processes, the renewable raw material wood could replace components made from energy-intensive or difficult-to-recycle materials.
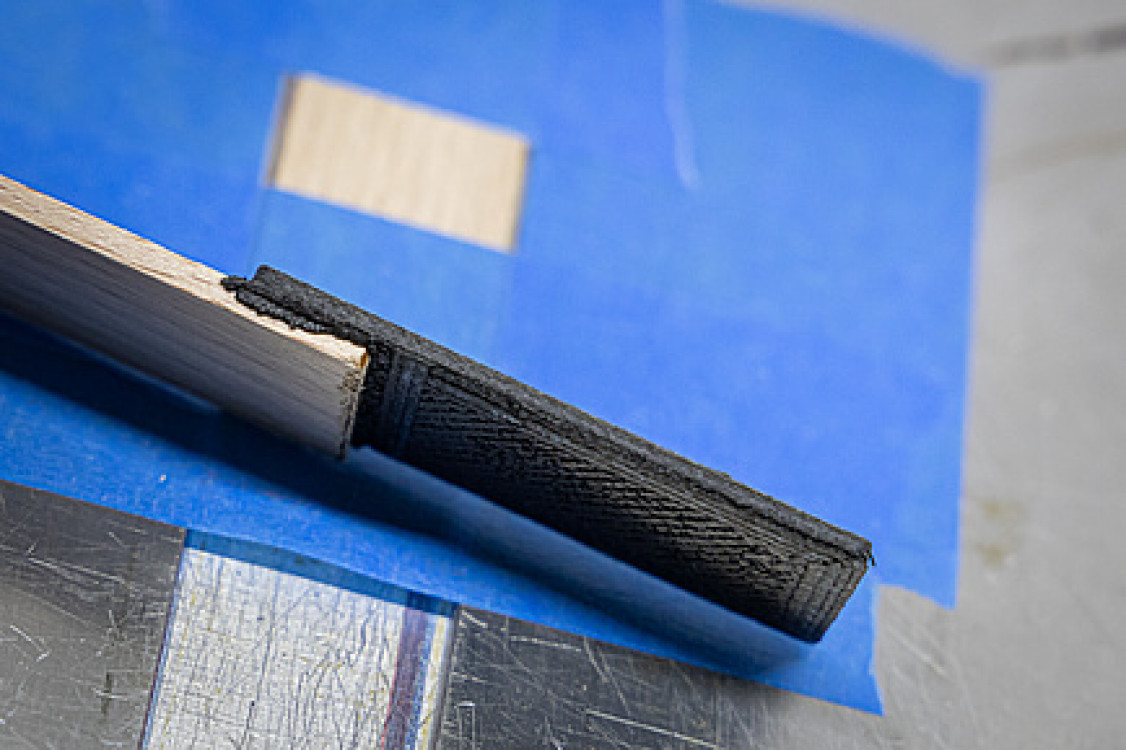

AddJoining: 3D printing leads to joining via the wood pores
With the AddJoining technique, a component made of polymer composite is affixed to and printed directly onto a surface – in this case wood – using a 3D printing process. The printed material penetrates into the wood pores, where a chemical reaction occurs, similar to the reaction of glue with wood. The resulting connections were highly successful in mechanical load tests. “After the joint fractured, we were able to find polymer in the wood pores and broken wood fibres in the polymer, which suggests that the fracture occurred in the wood and polymer, but not at the joint,” explains Gean Marcatto, who works on this process as a postdoc at the institute. These successful tests were carried out on the untreated wood surface. Even more durable joints could be achieved by introducing a micro- or nano-structure into the wood through laser texturing or etching, which increases the pores and enhances the bonding surfaces. “But we wanted to work with as few steps as possible and, above all, without chemicals,” says Sergio Amancio, explaining the underlying idea. “We can use this technology particularly well with complicated 3D geometries because the components are printed directly onto the surface – in whatever geometry is required.”

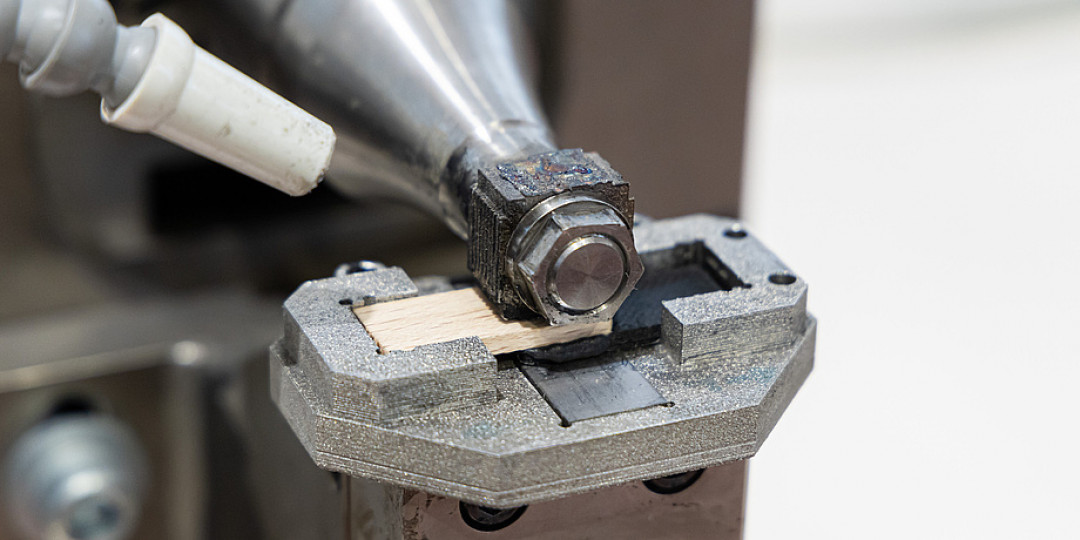
Ultrasonic joining ensures a stable spot joint
In Ultrasonic Joining, high-frequency vibration with low amplitude is applied to the wooden component using a sonotrode. In contact with the base component – in this case, polymer or a polymer composite material – the friction generates heat at the interface which melts the surface of the polymer part. Molten polymer infiltrates into the naturally porous surface of the wood. In this way, a very stable spot joint can be achieved, from a mixture of mechanical interlocking (because the melted plastic solidifies again in the wood) and adhesion forces. “This technique is particularly suitable for large components and 2D structures since we achieve a precisely localized spot joint,” explains Awais Awan, who dedicated his doctorate to joining technology using ultrasonic energy. These spot joints were also mechanically tested with great success. The joints could also be further strengthened by pre-treatment of the wood surface such as laser texturing.
(Source: TU Graz Press Release)
Schlagworte
Additive ManufacturingAMFrictional HeatJoiningLightweight ConstructionUltrasonic Construction